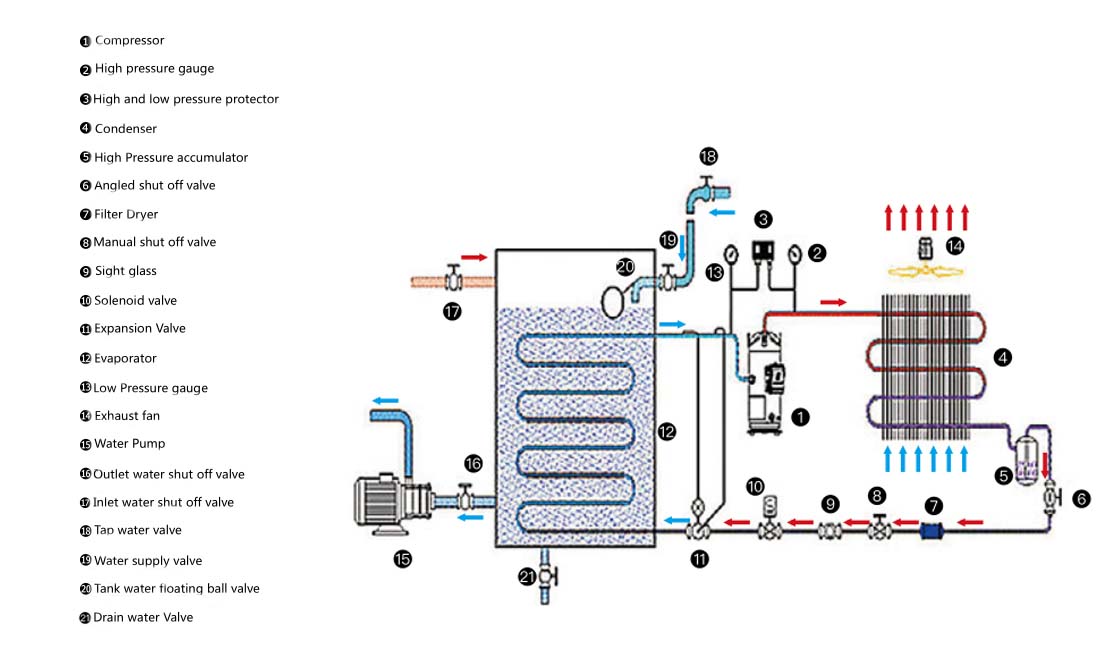
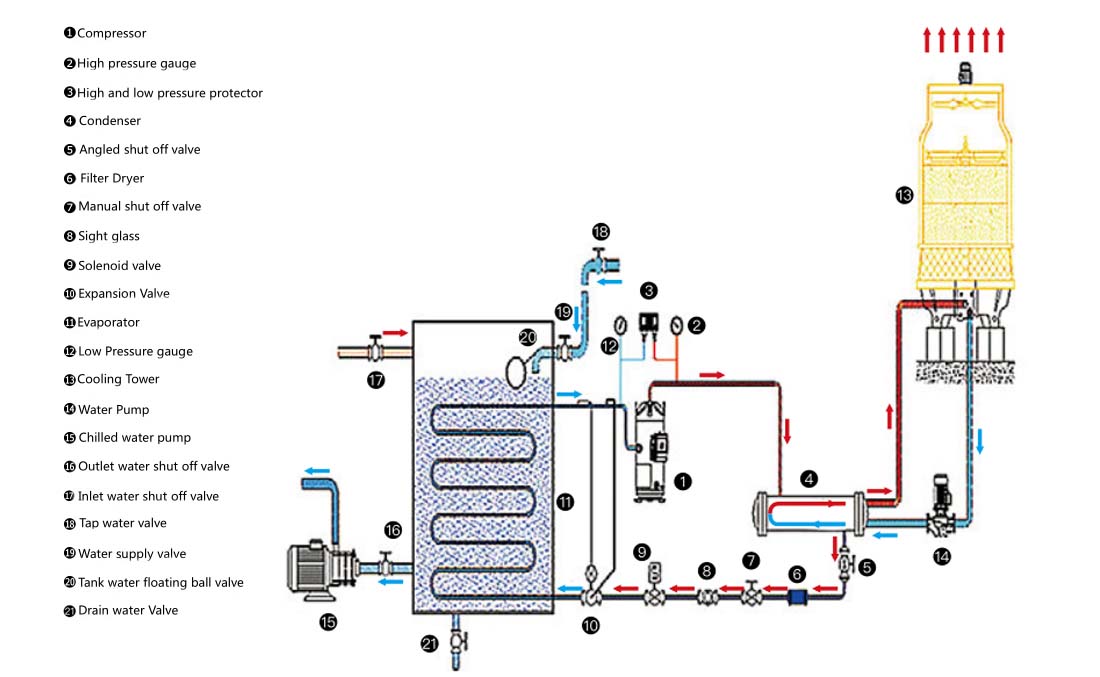
Commonly used auxiliary accessories for low temperature chillers, including water flow switch, pressure controller, pressure difference controller, temperature controller and solenoid valve, as well as a brief introduction of three cooling methods, liquid vaporization refrigeration, gas expansion refrigeration and thermoelectric refrigeration.
Common auxiliary accessories for low-temperature chillers
1, water flow switch
The water flow switch is used as the control or cut-off protection of the fluid flow in the pipeline. When the fluid flow reaches the set value, the switch automatically cuts off (or connects) the circuit.
2, pressure controller
The pressure controller is used for pressure control and pressure protection. The chiller has low and high pressure controllers to control the working range of the system pressure. When the system pressure reaches the set value, the switch automatically cuts off (or connects) the circuit.
3, differential pressure controller
The pressure difference controller is used to control the pressure difference. When the pressure difference reaches the set value, the switch automatically cuts off (or turns on) the circuit.
4, temperature controller
The temperature controller is used for the control or protection of the unit. When the temperature reaches the set value, the switch automatically cuts off (or turns on) the circuit. In our products, temperature control is often used, and the temperature of the water tank is used to control the startup and shutdown of the unit. There are also temperature controllers that need to be used for antifreeze.
5, solenoid valve
Cut off the system circuit when the compressor is stopped to avoid liquid shock when the compressor is started next time. It is generally used in a larger refrigeration system.
Three cooling methods
1. Liquid vaporization refrigeration:
1) Compression: The normal temperature gas state becomes a high pressure and high temperature gas state.
2) Condensation: High pressure and high temperature gas becomes high pressure liquid
3) Evaporation: High-pressure liquid turns into low-pressure gas, absorbing heat and realizing refrigeration.
2, gas expansion refrigeration:
Gas expansion refrigeration uses the adiabatic expansion of high-pressure gas to reach low temperature, and uses the reheating process of the expanded gas at low pressure to refrigerate. Due to the different equipment for gas adiabatic expansion, there are generally two ways: one is to increase the high pressure The gas is expanded by the expander and has external power output, so the temperature drop of the gas is large, and the cooling capacity is also large during reheating. However, the expander structure is more complicated. Another way is to make the gas expand through the throttle valve without external power output. The temperature drop is small and the cooling capacity is small, but the structure of the throttle valve is relatively simple, which is convenient for the adjustment of the gas flow.
3. Thermoelectric cooling
When the DC power supply is turned on, the current direction of the upper connector is N-P, the temperature decreases, and absorbs heat, forming a cold end; the current direction of the lower connector is p-n, the temperature rises, and heat is released, forming a hot end. Several pairs of thermocouples are connected to form a commonly used thermopile. With the help of various heat transfer devices, the hot end of the thermopile continuously dissipates heat and maintains a certain temperature, and the cold end of the thermopile is placed in the working environment to absorb Heat, produce low temperature, this is the working principle of semiconductor refrigeration. The solar semiconductor refrigeration system uses the thermoelectric cooling effect of semiconductors to directly supply the required DC power by solar cells to achieve the effect of cooling and heating.
If you need to know more about low-temperature chillers, glycol chillers, screw chillers, chillers, ice water chillers, scroll chillers, piston chillers and refrigerators and other refrigeration products, please contact our OUMAL refrigeration manufacturer, and we will try our best to solve the failure of the chiller for customers. Such as chiller does not refrigerate and other issues, wholeheartedly recommend customers to choose the right chiller products, so that everyone can buy the right machine and solve your industrial cooling water system issue. Welcome to consult us at any time. The oumal industrial chiller water unit adopts original imported configuration, fully automatic computer controller, which can precisely control the temperature of the coating machine. According to customer requirements, different methods of use are developed to produce refrigeration equipment that meets customer requirements to ensure the high quality of plating parts. .